A Primer on AI Smart Glasses
AI Smart Glasses: Understanding the Technology Breakthrough and Market Dynamics
The primer below attempts to better understand the current state of the AI Smart Glasses landscape, prospects, key players, technology development perspectives, and strategic implications.
Google I/O 2025: Google reframed the AI landscape, and Gemini is now the core intelligence layer. Search has evolved into a real-time reasoning engine. In parallel, the second era of smart glasses started. Google announced that it will partner with Samsung, Gentle Monster, and Warby Parker to create AI smart glasses that people want to wear. In the same week, OpenAI announced the acquisition of io, the product-development startup founded by renowned former Apple designer Jony Ive, in a deal valued at $6.5 billion. There were lots of rumors about what they were willing to build and whether they were building smart glasses, although specific details about upcoming products are still under wraps. The partnership is expected to focus on new AI-driven consumer devices; the goal is to create "less socially disruptive products than the iPhone."
I must admit that I wrote this text from the perspective of a longtime Dragon Ball manga fan and one of the devices Akira Toriyama introduced to the story: the Scouter, a device/monocle used to measure power levels and determine an opponent's location in the story. It was mainly used by Saiyans and members of Frieza's army. Since then, I've keenly seen smart glasses devices and rumors popping up.
Introduction: The Quiet Revolution in Wearable Computing
While the technology world debates the next major platform shift, Meta has achieved a genuine breakthrough with its Ray-Ban smart glasses, selling over 2 million units since their October 2023 launch. This success has sparked intense competition among technology giants and represents the most significant advancement in wearable computing since the smartphone era began.
To understand why this moment matters, we need to examine the convergence of three critical factors: technological maturity, market readiness, and competitive necessity. Unlike previous attempts at face-worn computing, current AI-powered smart glasses solve real problems while avoiding the social and technical pitfalls that doomed earlier efforts.
Understanding the Technology Foundation: Learning from Past Failures
The journey from Google Glass's spectacular failure to today's emerging success offers crucial insights into technology adoption patterns. Google Glass, launched in 2014 at $1,500, created more problems than it solved. The device was expensive, socially awkward (earning users the "Glasshole" label), technically limited with poor battery life, and raised genuine privacy concerns with its always-recording capabilities.
However, Google's fundamental insight about augmented human capabilities remained valid. The technology simply wasn't ready for mainstream adoption. This teaches us an important lesson about innovation timing: having the right vision without the supporting technology often leads to premature market entry and subsequent rejection.
The breakthrough came when three technological advances converged between 2024 and 2025. Modern artificial intelligence reached practical utility, moving beyond simple command execution to genuine contextual understanding. Edge computing advances enabled on-device processing that preserves privacy while reducing latency. Manufacturing improvements in micro-displays, batteries, and optics finally made comfortable all-day wearable computing possible.
This convergence resembles the smartphone revolution, where individual technologies like touchscreens, internet connectivity, cameras, and GPS existed separately before the iPhone combined them into something transformative. AI smart glasses represent a similar convergence moment, where existing technologies finally work together effectively.
Current Market Landscape
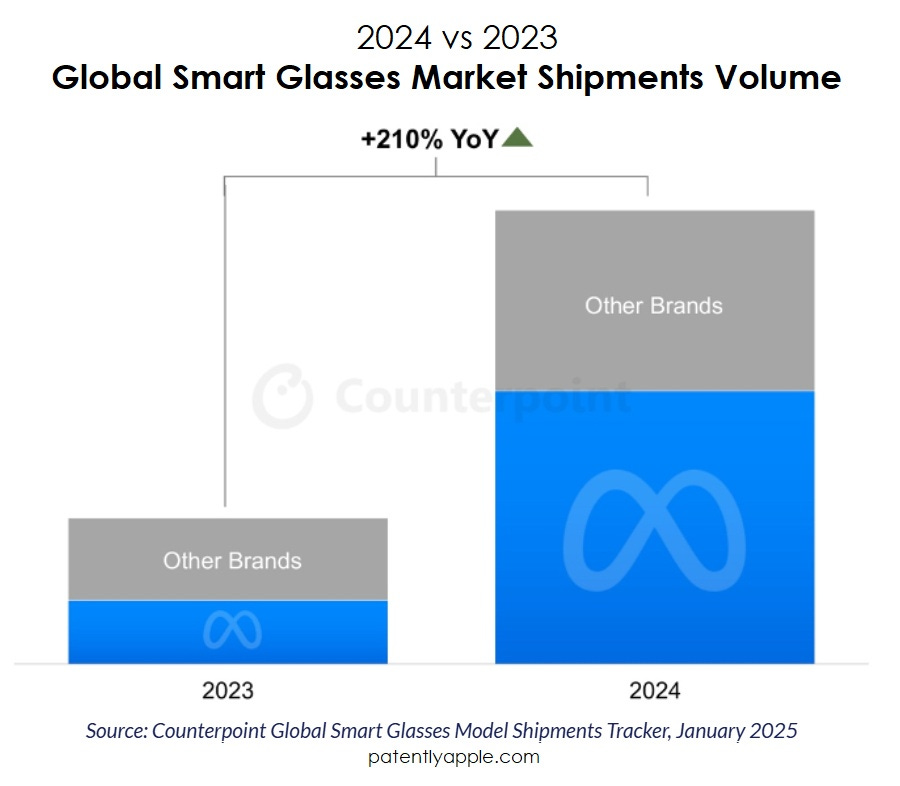
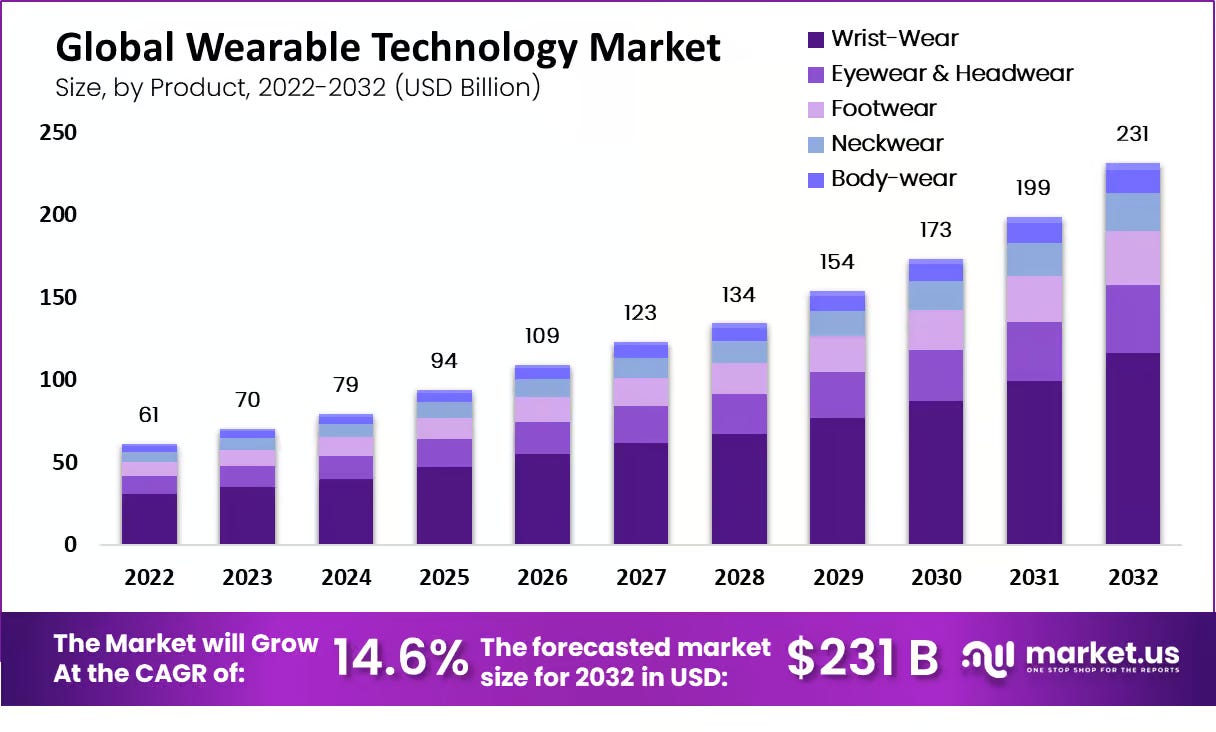
The smart glasses market has experienced unprecedented growth, with global shipments surging 210% in 2024, according to Counterpoint Research. The market crossed the 2-million-unit milestone for the first time, driven primarily by strong demand for Ray-Ban Meta smart glasses. Market research firm Grand View Research values the current smart glasses market at $1.93 billion in 2024, with projections reaching $8.26 billion by 2030, representing a compound annual growth rate of 27.3%.
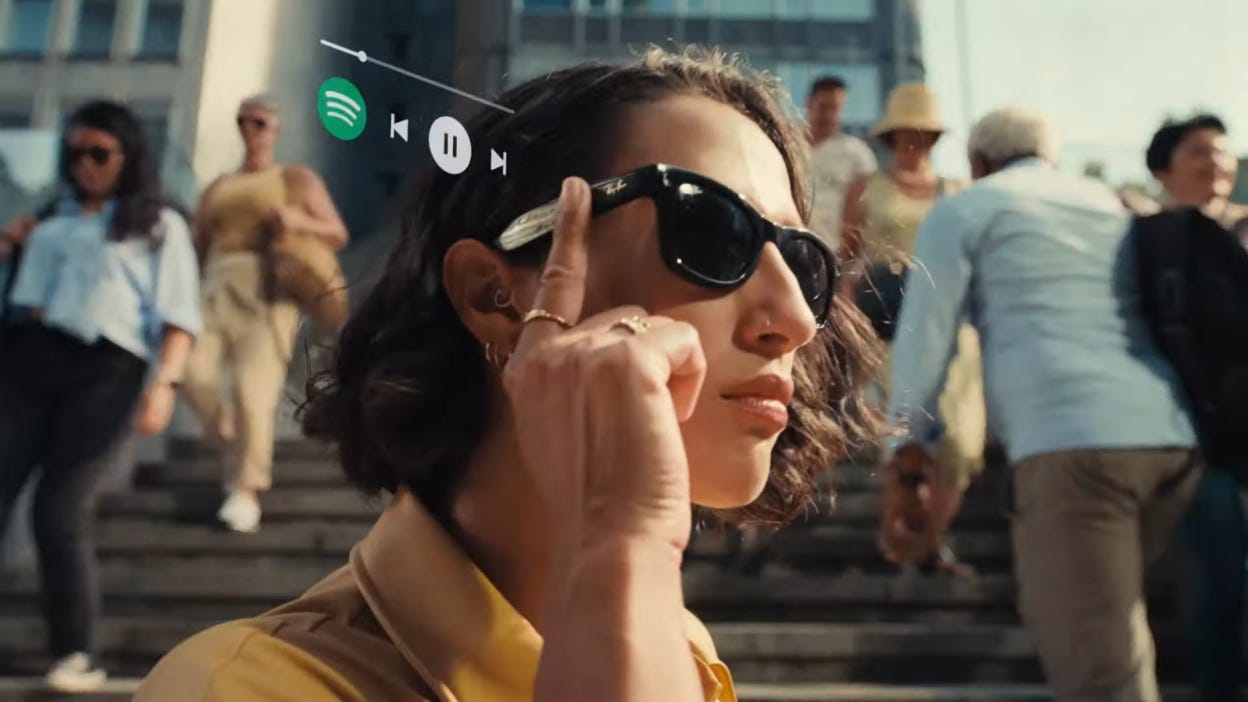
Meta's success with Ray-Ban smart glasses demonstrates that consumers will adopt face-worn technology when it's designed correctly and provides genuine utility. The glasses look like traditional Ray-Ban Wayfarers, eliminating the aesthetic concerns that plagued Google Glass. They offer practical features like hands-free photography, voice assistance, and audio content consumption without the complexity and privacy concerns of always-on video recording.
The competitive landscape now includes major players pursuing different strategies. Meta leads with consumer validation through its Ray-Ban partnership, proving market demand exists. Apple has reportedly accelerated its smart glasses development timeline from 2027 to late 2026, demonstrating the strategic importance of this category. Google pursues a platform strategy through Android XR, enabling multiple hardware partners rather than developing proprietary devices.
Chinese manufacturers, including Baidu, RayNeo, and numerous startups, have launched competitive products throughout 2024-2025, creating pricing pressure and feature innovation that benefits the entire market. This global competition ensures rapid technological advancement and market expansion.
How AI Transforms the Experience
AI-powered smart glasses recognize visual input continuously, understand context automatically, and provide assistance without explicit commands. Instead of taking a photo and manually requesting translation through multiple steps, the glasses recognize text automatically and provide instant translation while understanding you're looking at a menu. Based on your preferences, they might suggest popular dishes or identify ingredients you're allergic to. Checking info about historical monuments while traveling or checking how a restaurant is rated on Google Maps sounds like a perfect feature for me.
This represents a fundamental shift in human-computer interaction paradigms. Rather than adapting your behavior to technology limitations, the technology adapts to natural human patterns and environmental context. You're not operating a device but collaborating with an intelligent assistant that understands your situation and anticipates your needs. Eliminating the necessity of catching/ checking the phone is a game-changer.
The technical capabilities demonstrate remarkable sophistication that wasn't possible even two years ago. Modern multimodal AI processes visual information at high frame rates while simultaneously running natural language processing for voice commands and environmental audio analysis. Edge computing enables this processing locally on specialized chips, reducing privacy concerns while maintaining responsive performance.
Meta's approach integrates AI that analyzes visual input continuously, recognizes objects, reads text, and understands spatial relationships. When you open your refrigerator, the system can identify available ingredients and suggest recipes without being asked. When you look at landmarks while traveling, it provides historical context and practical information automatically.
Apple's strategy focuses on privacy-preserving on-device processing that maintains seamless ecosystem integration. Users can access Siri functionality, receive notifications, and interact with iPhone apps without compromising privacy or requiring constant internet connectivity.
Google's approach leverages superior language AI through Gemini integration, providing real-time translation, search capabilities, and environmental understanding. The Android XR platform enables multiple hardware manufacturers to access these AI capabilities while maintaining a consistent user experience across different devices.
Real-World Applications
Enterprise applications provide clearer return on investment calculations than consumer use cases. Boeing has documented significant productivity improvements by implementing AR glasses across assembly operations. Workers receive step-by-step visual instructions overlaid on their field of view, reducing assembly errors and training time. The hands-free interface allows technicians to access technical documentation, parts catalogs, and quality checklists without interrupting their workflow.
The logistics and warehousing sector shows measurable efficiency improvements that translate directly to competitive advantages. Major retailers and logistics companies report that smart glasses reduce package sorting errors while improving delivery accuracy. Workers receive visual picking instructions and inventory information without handheld devices, increasing throughput while reducing physical strain from constantly looking down at screens.
Consumer adoption centers on daily convenience and productivity enhancement rather than entertainment features. Early adopters report using smart glasses for commute audio content, quick photo capture throughout the day, and hands-free note-taking during meetings. The seamless integration means users interact less frequently with smartphones, which helps them stay present during family time and social interactions.
Content creators embrace first-person perspective capabilities that enable authentic storytelling that is impossible with traditional cameras. Social media creators use smart glasses for immersive travel content, cooking demonstrations, and behind-the-scenes footage that provides viewers with genuine first-person experiences.
Strategic Competition Among Technology Giants
Understanding the strategic thinking behind each major company's approach helps predict future market development. Meta's strategy reflects hard-earned lessons from missing the mobile platform transition. The company watched Apple and Google control smartphone ecosystems while Facebook remained dependent on their platforms and policies. Reality Labs' substantial investment (over $80 billion since 2014) represents a determination to avoid repeating that strategic mistake.
Meta's approach shows methodical platform development rather than rushed product launches. The company first established consumer acceptance through Ray-Ban partnerships, proving people will adopt face-worn technology when designed correctly. Current development focuses on introducing display capabilities through upcoming glasses targeting enterprise and productivity applications. Future phases will deliver true augmented reality through consumer versions, enabling immersive experiences that could justify smartphone replacement.
Apple's accelerated timeline reveals strategic urgency that is unusual for the company. Reports suggest Tim Cook compressed smart glasses development from 2027 to late 2026, representing the most aggressive product acceleration in Apple's history outside crisis response situations. Sources indicate Cook considers smart glasses his "top priority" from a product development standpoint.
Apple's competitive advantages center on ecosystem integration, which creates natural upgrade paths for existing customers. Smart glasses will initially function as iPhone accessories, leveraging the company's massive installed base and seamless connectivity. Privacy-preserving on-device AI processing appeals to customers who are increasingly concerned about data protection.
The challenge involves Siri's AI capabilities, which currently lag behind ChatGPT and Google's Gemini in multimodal understanding. Smart glasses succeed based on AI usefulness rather than hardware elegance, potentially undermining Apple's traditional differentiation strategy.
Google's platform strategy mirrors its successful Android smartphone approach while addressing different market dynamics. Rather than competing directly with hardware, Google provides AI capabilities and development tools that enable multiple manufacturers to create competitive products. This strategy leverages Google's AI advantages while avoiding massive hardware research and development investments.
Chinese manufacturers present competitive pressure through aggressive pricing and rapid innovation cycles. Throughout 2024-2025, companies often matched Western features at significantly lower prices. Government support for AI hardware development provides strategic advantages through subsidized research and favorable regulatory treatment.
Future Technology Roadmap and Market Evolution
The 2026-2027 timeline represents critical market convergence that will likely determine platform winners. Apple plans to launch consumer smart glasses in late 2026, directly competing with Meta's enhanced offerings and Google's expanding partner ecosystem. This convergence reflects technical maturity meeting market demand and competitive necessity.
Battery technology improvements will enable the transition from smartphone accessory to independent computing device. Current smart glasses provide several hours of continuous usage, but achieving truly independent all-day functionality requires significant advances in battery density, wireless charging, and power management.
Display technology evolution will expand from notification systems to immersive visual experiences. Current micro-displays struggle with outdoor visibility and provide a limited field of view. Next-generation waveguide technology and improved projection systems aim to deliver smartphone-quality visual experiences in lightweight glasses form factors.
Artificial intelligence capabilities will advance from reactive assistance to predictive intelligence that anticipates user needs. Future AI glasses will learn individual behavior patterns, understand contextual cues, and provide proactive assistance without explicit prompts. Integration with Internet of Things devices and smart city infrastructure will create environmental awareness that enhances daily navigation and interaction.
Social acceptance will normalize through gradual exposure, usability, and improved design aesthetics. Privacy concerns that plagued early smart glasses adoption should diminish as social norms develop around appropriate usage contexts and recording consent protocols. Visual indicators for recording status and established etiquette guidelines will address current concerns about surveillance and privacy violations.
The integration of prescription eyewear represents a massive market expansion opportunity. Approximately 64% of adults use corrective lenses, creating natural adoption paths for smart glasses that combine vision correction with computing capabilities. Partnerships between technology companies and eyewear manufacturers will accelerate this integration.
Platform consolidation will likely create two to three dominant ecosystems by 2030, similar to smartphone market dynamics. Winner-take-most effects will favor companies with the strongest ecosystem integration, developer support, and manufacturing partnerships.
Challenges and Potential Barriers
Every transformative technology faces significant obstacles before achieving mainstream adoption. Battery life constraints represent the most fundamental technical limitation, affecting every other aspect of user experience. Current AI processing demands require significant power consumption, which conflicts with lightweight, all-day wearable requirements.
Privacy and social acceptance concerns echo the "Glasshole" phenomenon that affected Google Glass adoption. Many people remain uncomfortable with devices that could record conversations or capture images without an obvious visual indication. Building social trust requires transparent privacy controls, clear recording indicators, and established etiquette around appropriate usage contexts.
Manufacturing complexity and cost present scalability challenges that could limit market expansion. Advanced waveguides, custom silicon, and precision optics require specialized manufacturing capabilities that few suppliers can deliver at volume. Component costs remain high due to limited production scale and requirements for technical sophistication.
Display quality and field of view limitations affect user experience in ways that may not be immediately obvious. Micro-displays currently struggle with brightness levels needed for outdoor visibility while maintaining acceptable battery life. Field of view restrictions limit immersive AR applications that justify premium pricing and learning curves.
Regulatory uncertainty creates compliance complexity that varies across international markets. Different countries approach AI governance, data protection, and safety standards differently. Smart glasses that collect visual and audio data must comply with privacy regulations while meeting safety requirements for wearable devices.
Strategic Implications
The AI smart glasses transformation creates opportunities and risks that will affect individuals, businesses, and investors differently depending on their positioning during this platform transition. For individual consumers, timing considerations depend on technology adoption preferences and specific use case priorities.
Early adopters should consider Meta's Ray-Ban glasses for proven functionality and established ecosystem support at reasonable pricing that offers accessible entry into AI-powered wearable computing. If you primarily use Apple devices and value ecosystem integration highly, waiting for Apple's 2026 launch may provide better seamless connectivity and privacy features. The workflow between the whole Google ecosystem and Gemini might be the most useful experience for the users.
The key insight involves recognizing that smart glasses represent a genuine platform transformation rather than an incremental technology improvement. The individuals, businesses, and investors who position themselves thoughtfully during this transition period will benefit most from the substantial value creation that accompanies major technology platform shifts.
Understanding these dynamics helps explain why technology companies have invested tens of billions of dollars in smart glasses development during 2024-2025. They're not building better gadgets but competing for position in computing's next platform, with the potential to reshape how humans interact with digital information and services in their daily lives.